Identify and Describe the Three Types of Genetic Modification
The processes of evolution Selection mutation migration and more. Three possible types of small-scale mutations may occur.
What Is Genetic Modification Curious
Microevolution Evolution within a population.
. Macroevolution Evolution above the species level. Down syndrome is a chromosomal disorder. Its still a very broad term as there are many different techniques and technologies used each with their own advantages and.
A genetically modified organism GMO is an animal plant or microbe whose DNA has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. Furthermore in the same field genetically modified plants are created to. Slide 5 Also referred to as a point mutation substitutions occur when a nucleotide is replaced with a different nucleotide in the DNA sequence.
Chromosomal disorders where chromosomes or parts of chromosomes are missing or changed. The location of the section of DNA containing the gene for making the human protein insulin must be identified it. IRinsect resistant HTherbicide tolerant DTdrought tolerant VRvirus resistant.
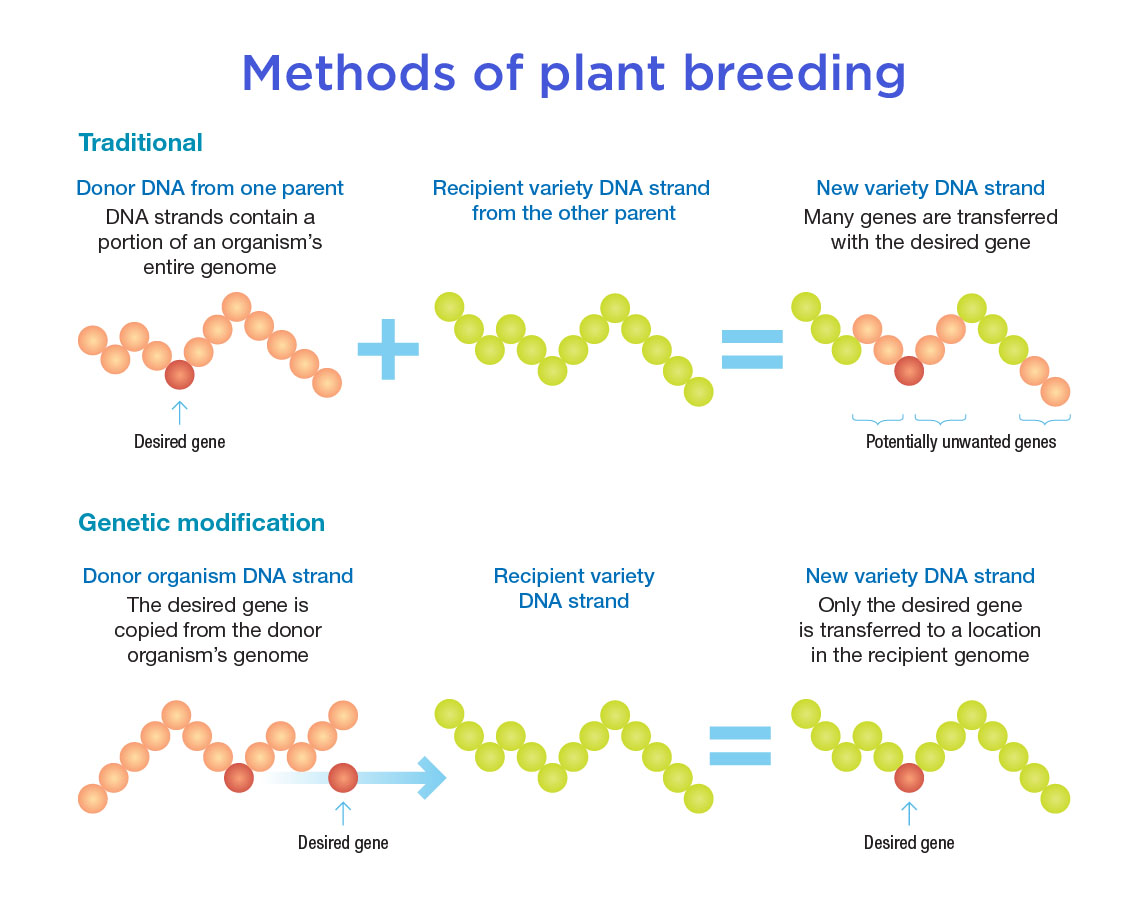
Human genetic modification or gene editing can be used in two very different ways. Mutations are changes in the information contained in genetic material. Types of Genetic Modification Methods for Crops Traditional Crop Modification.
Traditional methods of modifying plants like selective breeding and crossbreeding have. Somatic genome editing changes the genes in a patients cells to treat a medical condition. Genetic modification is the process of altering the genetic makeup of an organism.
Living or once-living thing. This type of variant may alter the function of the protein made from the gene. Genetic engineering is a method that among other things enables scientists to copy a gene with a.
Speciation How new species arise. Without genetic variation some key mechanisms of evolutionary change like natural selection and genetic drift cannot operate. For thousands of years humans have used breeding methods to modify organisms.
Polycationic neutralization of the cell membrane and the DNA to be introduced to improve passive uptake. Substitutions deletions and insertions. Genetically modified organisms GMOs are produced using scientific methods that include recombinant DNA technology and reproductive cloning.
Genetic modification also referred to as genetic engineering refers to the process of changing the DNA of a living organism with the aim of altering its characteristics. 9 rows Deletion duplication translocation and inversion are some of the common types of mutations. Process by which organisms that are better -adapted to their environments produce more offspring to transmit their genetic characteristics.
There are three types of genetic disorders. The replacement of a DNA component as part of genetic modification. Single-gene disorders where a mutation affects one gene.
Currently grown GM crops in the US traits for which they are modified and percent of total acreage of the crop that is planted to GM varieties. A few gene therapies are approaching clinical use but remain extraordinarily expensive. Unlike traditional breeding in animals and plants genetic modification involves inserting a gene from one.
Commonly used methods include. For most of life this means a change in the sequence of DNA. The Golden rice is one of the oldest GM crops in the world and the last one on our list of 10 examples of.
Corn cattle and even dogs have been selectively bred over generations to have certain desired traits. Electroporation where DNA is introduced through cell membrane pores by pulsed electrical charges. This has been done indirectly for thousands of years by controlled or.
In reproductive cloning a nucleus is extracted from a cell of the individual to be cloned and is inserted into the enucleated cytoplasm of a host egg an enucleated egg is an egg cell that has had its. By contrast heritable genome editing would change genes in eggs sperm or early embryos to try. The big issues Pacing diversity complexity and trends.
Microinjection of DNA into the nucleus of anchored cells. In-plant biotechnology and agriculture pesticidal herbicidal drought temperature insecticidal and other abiotic stress-resistant plant species can be created. There are three primary sources of new genetic variation.
A reading frame consists of groups of three nucleotides that each code for one amino acid. Sudden variation in one or more characteristics caused by a change in a gene or chromosome. An inversion changes more than one nucleotide in a gene by replacing the original sequence with the same sequence in reverse order.
Chromosomes are the structures that hold our genes. The stages of genetic engineering. Sickle cell anemia is an example.
The term genetic modification is now generally understood by many people to refer specifically to these modern technologies and their role in developing genetically modified organisms GMOs and products.

Types Of Genetic Modification Methods For Crops Fda
Types Of Genetic Modification Methods For Crops Fda

Gmos The Scarlet Letters Of The Grocery Aisle Medill Reports Chicago

Genetically Modified Organisms The Good The Bad And The Future Science In The News
0 Response to "Identify and Describe the Three Types of Genetic Modification"
Post a Comment